Regular readers will know that I have queried how insurance-linked securities (ILS) funds, currently so popular with pensions funds, can produce a return on equity that is superior to that of a diversified property catastrophe reinsurer given that the reinsurer only has to hold a faction of its aggregate limit issued as risk based capital whereas all of the limits in ILS are collaterised. The recent FT article which contained some interesting commentary from John Seo of Fermat Capital Management got me thinking about this subject again. John Seo referred to the cost advantage of ILS funds and asserted that reinsurers staffed with overpaid executives “can grow again, but only after you lay off two out of three people”. He damned the traditional sector with “these guys have been so uncreative, they have been living off earthquake and hurricane risks that are not that hard to underwrite.”
Now, far be it from me to defend the offshore chino loving reinsurance executives with a propensity for large salaries and low taxation. However, I still can’t see that the “excessive” overheads John Seo refers to could offset the capital advantage that a traditional property catastrophe reinsurer would have over ILS collateral requirements.
I understood the concept of ILS structures that provided blocks of capacity at higher layers, backed by high quality assets, which could (and did until recently) command a higher price than the traditional market. Purchasers of collaterised coverage could justify paying a premium over traditional coverage by way of large limits on offer and a lower counterparty credit risk (whilst lowering concentration risk to the market leading reinsurers). This made perfect sense to me and provided a complementary, yet different, product to that offered by traditional reinsurers. However, we are now in a situation whereby such collaterised reinsurance providers may be moving to compete directly with traditional coverage on price and attachment.
To satisfy my unease around the inconsistency in equity returns, I decided to do some simple testing. I set up a model of a reasonably diversified portfolio of 8 peak catastrophic risks (4 US and 4 international wind and quake peak perils). The portfolio broadly reflects the market and is split 60:40 US:International by exposure and 70:30 by premium. Using aggregate exceedance probability (EP) curves for each of the main 8 perils based off extrapolated industry losses as a percentage of limits offered across standard return periods, the model is set up to test differing risk premiums (i.e. ROL) for each of the 8 perils in the portfolio and their returns. For the sake of simplicity, zero correlations were assumed between the 8 perils.
The first main assumption in the model is the level of risk based capital needed by the property catastrophe reinsurer to compete against the ILS fund. Reviewing some of the Bermudian property catastrophe players, equity (common & preferred) varies between 280% and 340% of risk premiums (net of retrocessions). Where debt is also included, ratios of up to 400% of net written premiums can be seen. However, the objective is to test different premium levels and therefore setting capital levels as a function of premiums distorts the results. As reinsurer’s capital levels are now commonly assessed on the basis of stressed economic scenarios (e.g. PMLs as % of capital), I did some modelling and concluded that a reasonable capital assumption for the reinsurer to be accepted is the level required at a 99.99th percentile or a 1 in 10,000 return period (the graph below shows the distribution assumed). As the graph below illustrates, this equates to a net combined ratio (net includes all expenses) of the reinsurer of approximately 450% for the average risk premium assumed in the base scenario (the combined ratio at the 99.99th level will change as the average portfolio risk premium changes).
click to enlarge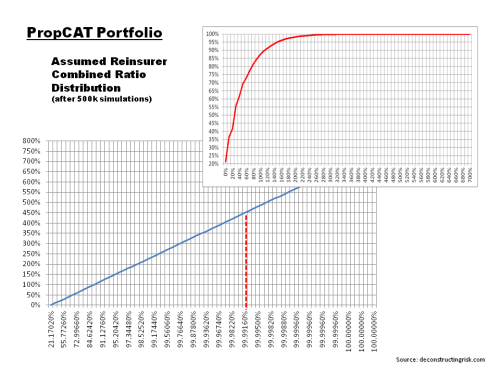
So with the limit profile of the portfolio is set to broadly match the market, risk premiums per peril were also set according to market rates such that the average risk premium from the portfolio was 700 bps in a base scenario (again broadly where I understand the property catastrophe market is currently at).
Reviewing some of the actual figures from property catastrophe reinsurer’s published accounts, the next important assumption is that the reinsurer’s costs are made up of 10% acquisition costs and 20% overhead (the overhead assumption is a bit above the actual rates seen by I am going high to reinforce Mr Seo’s point about greedy reinsurance executives!) thereby reducing risk premiums by 30%. For the ILS fund, the model assumes a combined acquisition and overhead cost of just 10% (this may also be too light as many ILS funds are now sourcing some of their business through brokers and many reinsurance fund managers share the greedy habits of the traditional market!).
The results below show the average simulated returns for a reinsurer and an ILS fund writing the same portfolio with the expense levels as detailed above (i.e 30% versus 10%), and with different capital levels (reinsurer at 99.99th percentile and the ILS fund with capital equal to the limits issued). It’s important to stress that the figures below do not included investment income so historical operating ROEs from property catastrophe reinsurers are not directly comparable.
click to enlarge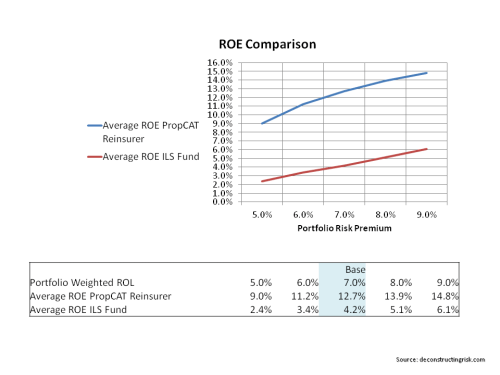
So, the conclusion of the analysis re-enforces my initial argument that the costs savings cannot compensate for the leveraged nature of a reinsurer’s business model compared to the ILS fully funded model. However, this is a simplistic comparison. Why would a purchaser not go with a fully funded ILS provider if the product on offer was exactly the same as that of a reinsurer? As outlined above, both risk providers serve different needs and, as yet, are not full on competitors (although this may be the direction of the changes underway in the market currently).
Also, many ILS funds likely do use some form of leverage in their business model whether by way of debt or retrocession facilities. And competition from the ILS market is making the traditional market look at its overhead and how it can become more cost efficient. So it is likely that both business models will adapt and converge (indeed, many reinsurers are now also ILS managers).
Notwithstanding these issues, I can’t help conclude that (for some reason) our pension funds are the losers here by preferring the lower returns of an ILS fund sold to them by investment bankers than the higher returns on offer from simply owning the equity of a reinsurer (admittedly without the same operational risk profile). Innovative or just cheap risk premia? Go figure.