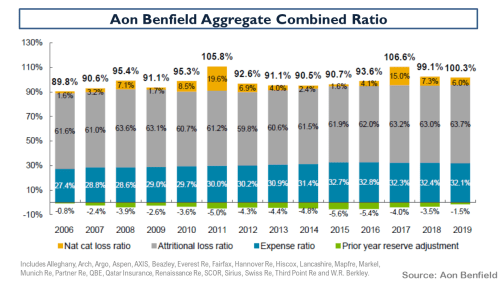
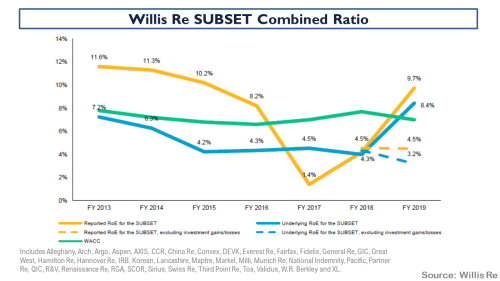
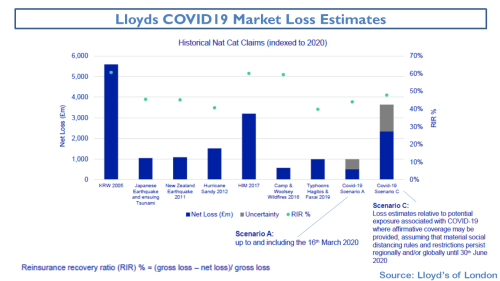
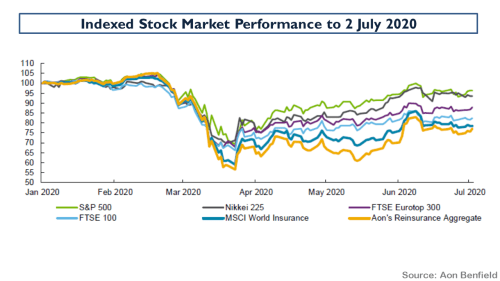
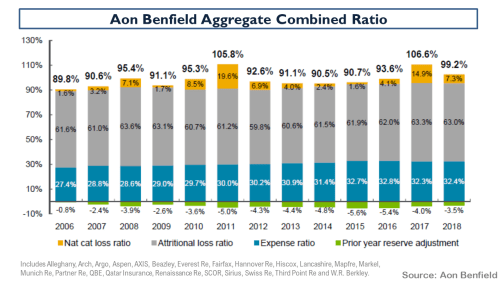
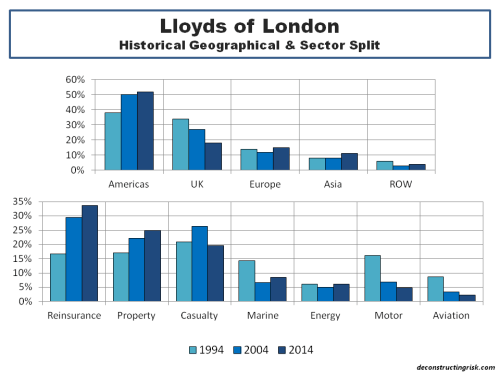
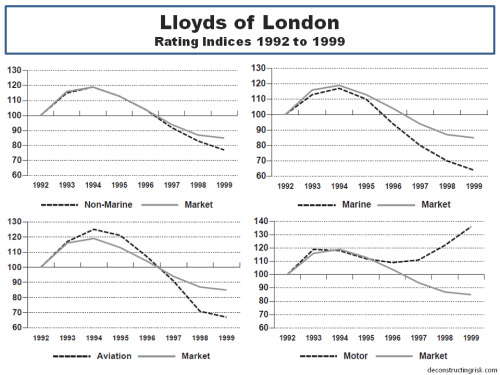
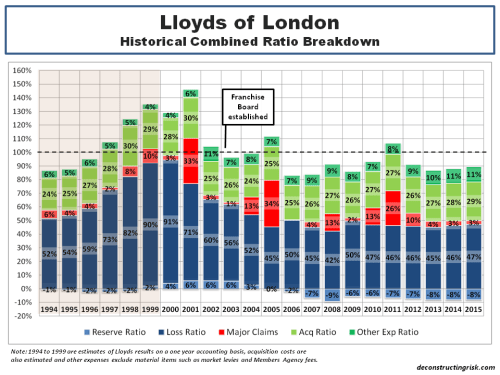
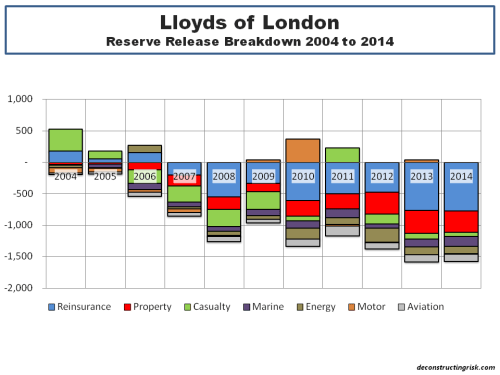
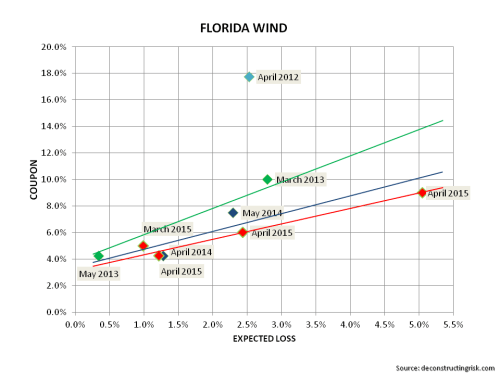
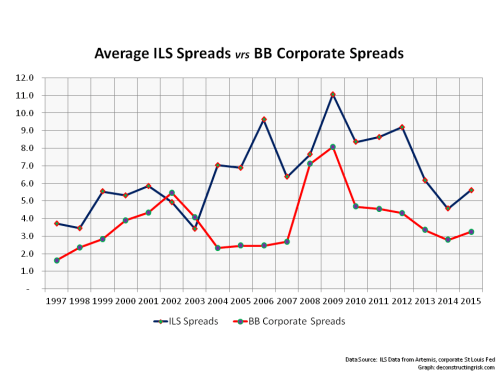
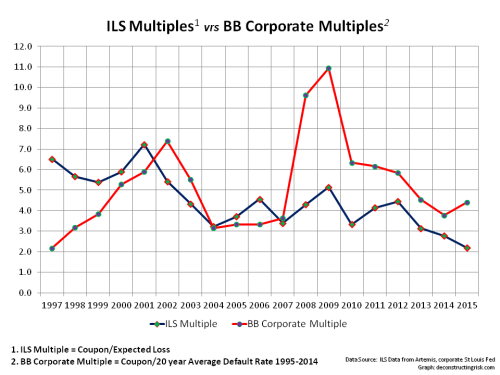
My negativity on the operating prospects for the reinsurance and specialty insurance sector has been articulated many times previously in this blog. Many of the same factors are impacting the broader commercial insurance market. Pricing conditions in the US and globally can be seen in the graph below.
click to enlarge
Two insurers, at different ends of the size scale, which I have previously posted on, are AIG (more recently here and here) and Lancashire (more recently here and here). Given that a lot has happened to each since I last posted on them, I thought a quick update on both would give an interesting insight into the current market.
First up is AIG who have been under a lot of pressure from shareholders to unlock value, including a break-up plan for the insurance giant from the opportunistic rascal Carl Icahn. The graph below shows a breakdown of recent operating results (as ever with AIG longer term comparisons are hampered by their ever changing reporting segments). The improvement in the UGC mortgage insurance business has been dwarfed by the poor non-life results which were impacted by a significant reserve strengthening charge.
click to enlarge
In January, Peter Hancock (the 5th CEO since Hank Greenberg left in 2005) announced a new strategic plan to the end of 2017, the main points of which are
- Return at least $25 billion of capital to shareholders through dividends and share buy-backs from operating profits, divestitures and other actions such as monetizing future life profits by $4-5 billion through reinsurance purchases.
- Enhance transparency by separating into an operating portfolio with a goal of over 10% return on equity and a legacy portfolio that will focus on return of capital. Reorganize into at least nine modular, more self-contained business units to enhance accountability, transparency, and strategic flexibility.
- Reduce general operating expenses by $1.6 billion, 14 percent of the 2015 expenses.
- Improve the commercial P&C accident year loss ratio by six points.
- Pursue an active divestiture program, including initially the 20% IPO of UGC.
The non-life reserve charge in 2015 amounted to $3.6 billion. 60% of the charge came from the (mainly US) casualty business, 16% from financial lines (again mainly in the US) and 15% from the run-off business. After the last material reserve strengthening in 2010, the worrying aspect of the 2015 charge is that approximately two thirds comes from accident years not yet 10 years old (which is relatively immature for long tail casualty business particularly when 42% of the charge is on excess casualty business). The impact of the reserve hikes on the commercial P&C segment can be clearly seen in the graph below.
click to enlarge
Perhaps the most aggressive target, given current market conditions, in the strategic plan is the 6% improvement in the commercial P&C accident year loss ratio by the end of 2017. The plan includes exiting approximately $1 billion of US casualty business, including poorly performing excess casualty business, primary and excess auto liability, health-care and financial lines business. Growth of $0.5 billion is been targeted in multi-national, financial lines, property upper middle market and major accounts which involve specialist engineering capabilities, international casualty and emerging risks such as cyber and M&A insurance. AIG also recently announced a two year reinsurance deal with Swiss Re on their US casualty book (it looks like a 25% quota share). The scale of the task for AIG in meeting this target can be seen in the exhibit below which takes a number of slides from the strategy presentation.
click to enlarge
I was struck by a quote from the firm on their turnaround plan – “We will use the data and analytical tools we have invested in to significantly differentiate and determine where we should focus our resources.” I suspect that every significant insurer would claim to have, or at least aspire to have, similar analytical capabilities. Big data and analytical driven underwriting is undoubtedly the future for large insurers with access to large amounts of quality data. Fortune had an interesting recent article on the analytical firm Palantir who are working with some insurers on sharpening their underwriting criteria for the social media age. An analyst in Citi even suggested that Goggle should look at buying AIG as a fintech play. The entry of the big internet firms into the insurance sector seems inevitable in some form or other, although I doubt AIG will be part of any such strategy.
As to the benefits of staying a large composite insurer, AIG cited an analysis commissioned by consultants Oliver Wyman supporting the benefits of diversification between the life and non-life business of AIG. Using the S&P consolidated model as a proxy, Oliver Wyman estimate a $7.5 billion capital benefit to AIG compared to separate life and non-life businesses, as envisaged in Icahn’s plan.
So, can AIG achieve the aggressive operational targets they have set themselves for the P&C business? Current market conditions present a considerable challenge. Combined with their recent results, an end of 2017 target for a 6% improvement is extremely aggressive. Too aggressive for my liking. However, the P&C results should improve somewhat over the short term (particularly if there is no more big reserve charges) and actions such as expense reductions, monetizing future life profits and divestitures will give AIG the fire power to hand out sweeties to shareholders. For those willing to take the punt, the return of a chunk of the $25 billion target in dividends and share buy-backs over the next 2 years for a firm with a current market value of $61 billion, trading at a 0.72 multiple to book value (trading around 0.92 of book less AOCI and DTA), may be too tempting to resist. It does have a certain allure…..
Lancashire, a London market specialty insurer and reinsurer with a mantra of disciplined underwriting, is at the opposite end of the scale spectrum with a niche focus. Long cherished by investors for its shareholder friendly dividend policies, Lancashire has been under pressure of late due to the heavy competition in its niche markets. The energy insurance sector, for example, has been described by the broker Willis as dismal with capacity chasing a smaller premium pool due to the turmoil in the oil market. A number of recent articles (such as here and here) highlight the dangers. Alex Maloney, the firm’s CEO, described the current market as “one of the most difficult trading environments during the last twenty years”. In addition, Lancashire lost its founder, Richard Brindle, in 2014 plus the CEO, the CFO and some senior underwriters of its Lloyds’ Cathedral unit in 2015.
The graph below shows the breakdown of reported historical calendar year combined ratios plus the latest accident year net loss ratio and paid ratio.
click to enlarge
The underwriting discipline that Lancashire professes can be seen in the recent accident year loss ratios and in the 30% drop in gross written premiums (GWP), as per the graph below. The drop is more marked in net written premiums at 35% due to the increase in reinsurance spend to 25% of GWP (from approx 10% in its early years).
click to enlarge
The timely and astute increase in reinsurance protection spend can be seen in the decrease in their peak US aggregate exposures. The latest probable maximum loss (PML) estimates for their US peak exposures are approximately $200 million compared to historical levels of $300-350 million. Given the lower net premium base, the PML figures in loss ratio terms have only dropped to 40% from 50-60% historically. Lancashire summed up their reinsurance purchasing strategy as follows:
“Our outwards reinsurance programme provides a breadth and depth of cover which has helped us to strengthen our position and manage volatility. This helps us to continue to underwrite our core portfolio through the challenges posed by the cycle.”
As with AIG, the temptation for shareholders is that Lancashire will continue with their generous dividends, as the exhibit below from their Q4 2015 presentation shows.
click to enlarge
The other attraction of Lancashire is that it may become a take-over target. It currently trades at 1.4 times tangible book level which is rich compared to its US and Bermudian competitors but low compared to its peers in Lloyds’ which trade between 1.58 and 2.0 times tangible book. Lancashire itself included the exhibit below on tangible book values in its Q4 2015 presentation.
click to enlarge
It is noteworthy that there has been little activity on the insurance M&A front since the eye boggling multiples achieved by Amlin and HCC from their diversification hungry Japanese purchasers. Many in the market thought the valuations signaled the top of the M&A frenzy.
Relatively, AIG looks more attractive than Lancashire in terms of the potential for shareholder returns. However, fundamentally I cannot get away from current market conditions. Risk premia is just too low in this sector and no amount of tempting upside through dividends, buy-backs or M&A multiples can get me comfortable with the downside potential that comes with this market. As per the sentiment expressed in previous posts, I am happy with zero investment exposure to the insurance sector right now. I will watch this one play out from the sidelines.