Munich Re had a good set of results last week with a 12.5% return on equity on a profit of €3.3 billion (with the reinsurance business contributing €2.8 billion of the profit). A €1 billion share buyback was also announced contributing to the ongoing shareholder friendly actions by industry players. Munich is targeting €3 billion for 2014 but warned of challenges ahead including “the lingering low-interest-rate environment, increasing competition in reinsurance, and changes in demand from clients in primary insurance”.
Torsten Jeworrek, Munich Re’s Reinsurance CEO, cited tailor-made solutions as a strength for Munich highlighting “multi-year treaties (occasionally incorporating cross-line and cross-regional covers), retroactive reinsurance solutions, transactions for capital relief, comprehensive consultation on capital management, and the insurance of complex liability, credit and large industrial risks”.
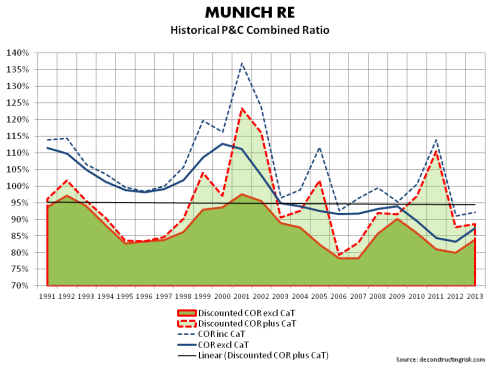
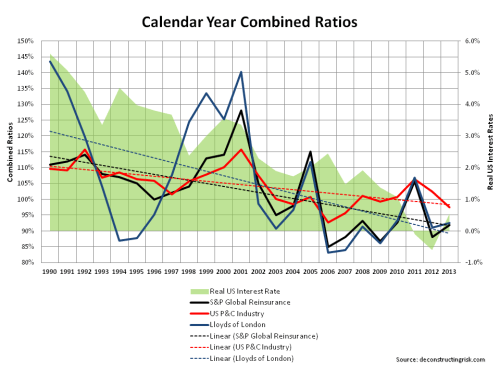
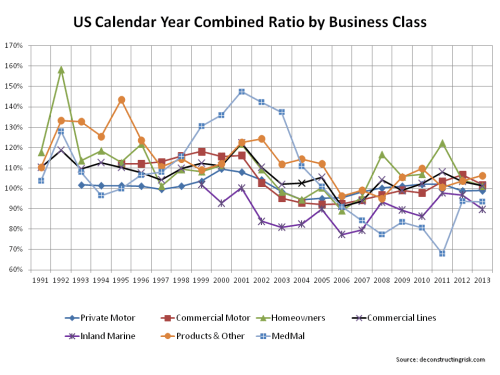
Whilst looking through the 2013 report, I noticed historical calendar year combined ratios (COR) for the P&C business (reinsurance & primary) including and excluding catastrophes. I dug up these figures going back to 1991 as per the graph below. A small amount of adjustment was needed, particularly in relation to the 24.3% and 17.1% of deterioration for 2001 and 2002 relating to 9/11 losses (which I included as catastrophes in the CaT ratio for those years). As with a previous post on underwriting cycles, I then “normalised” the COR excluding catastrophes for the changes in interest rates using a crude discount measure based upon the US risk free rate for each calendar year plus 150 bps over 2.5 years. That may be conservative, particularly for the 1990s where equities were a bigger part of European’s asset portfolio. I then added the (undiscounted) CaT ratio to the discounted figures to give an idea of the historical underwriting cycle.
The “normalised” average discounted COR (excluding CaT) since 1991 is 87% and the average over the past 10 years is 83%. The standard deviation for the series since 1991 is 6% and for the last 10 years 4% indicating a less volatile period in recent years in core ratios excluding catastrophes.
The average CaT ratio since 1991 is 7% versus 9% over the past 10 years. The standard deviation for the CaT ratio since 1991 is 8% and for the last 10 years 9% indicating a more volatile period in recent years in CaT ratios.
Adding the discounted CORs and the (undiscounted) CaT ratios, the average since 1991 and over the past 10 years is 95% and 92% respectively (with standard deviation of 11% and 9% respectively).
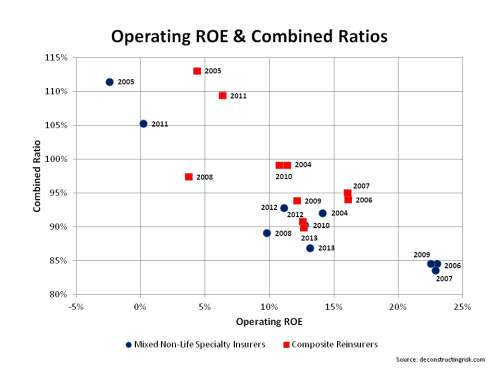
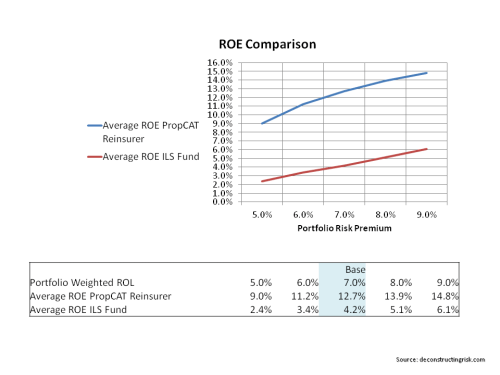
As Munich is the largest global reinsurer, the ratios (reinsurance & primary split approx 80%:20%) above represent a reasonable cross section of industry and give an average operating return of 5% to 8% depending upon the time period selected. Assuming a 0.5% risk free return today, that translates into a rough risk adjusted return as per the Sharpe ratio of 0.44 and 0.80 for the period to 1991 and over the past 10 years respectively. Although the analysis is crude and only considers operating results, these figures are not exactly earth-shattering (even if you think the future will be more like the last 10 years rather than the longer term averages!).
Such results perhaps explain the growing trend of hedge funds using reinsurance vehicles as “float” generators. If the return on assets over risk free is increased from the 150 bps assumed to 300 bps in the analysis above, the Sharpe ratios increase to more acceptable 0.73 and 1.13 respectively. And that ignores the tax benefits amongst other items!
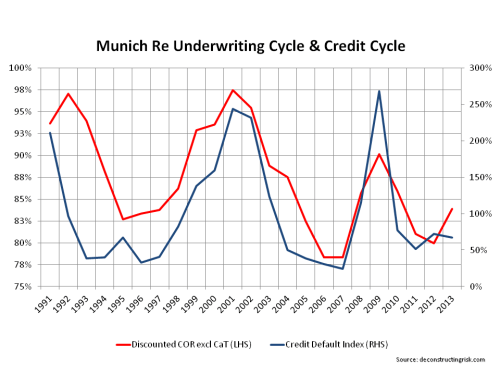
As an aside, I again (as per this post) compared the underlying discounted COR (excluding catastrophes) from Munich against a credit index of global corporate defaults (by originating year as a percentage of the 1991 to 2013 average) in the graph below. As a proxy for the economic & business cycles, it illustrates an obvious connection.