In the last post on this topic, I highlighted how new technologies, broadly under the fintech tag, had the potential to disrupt the banking sector, primarily by means of automating processes rather than any major reinventing of business models (although I did end that post with a bit of a rant about innovation and human behaviour). Blockchain is the hot topic that seems to be cropping up everywhere (I’ll leave that for another time). This post is about insurance and new technology, or in the jargon, insurtech.
The traditional business model in the insurance industry is not reacting well to a world of low or negative interest rates. For the life insurance sector, the duration mismatch between their liabilities and their assets is having a perverse impact as interest rates have fallen. Savings returns for aging populations have been sacrificed in Central Bank’s attempt to stimulate economic growth.
In addition, the traditional distribution channel for selling life insurer’s products, and the old adage is that these products are sold rather than bought, has relied too heavily on aging tied agents whose focus is on the wealthy client that can generate more fees than the middle class. The industry is generally at a loss on how to sell products in a low interest world to the mass market and to the new tech savvy generation. As a result, the industry and others are throwing money at a rash of new start-ups in insurance, as the exhibit on some of the current hyped firms focusing on life insurance below illustrates.
As the exhibit illustrates, the focus of these new start-ups is weighted towards technologies around product development, distribution, and underwriting. Some will likely succeed in trying to differentiate further the existing clientele of life insurers (e.g. real time health data). Many will be gobbled up or disappear. Differing attitudes between those aged under 34 and the older generation towards online distribution channels can be clearly seen in the survey results in the exhibit below.
With longevity and low interest rates the dominant challenges for life insurers today, automation of processes will assist in cutting expenses in the provision of products (mainly to the existing customer base) but will not likely meaningfully address the twin elephants in the room. Citigroup reckons that in 20 of the largest OECD countries the unfunded government liability for pensions is around $78 trillion which compares to approximately $50 trillion in GDP for all OECD countries in 2015. I look forward to conversing with a robo-advisor in the near future on what products it recommends for that problem!
Insurance itself is hundreds of years old and although the wonderfully namely bottomry (the earliest form of marine hull insurance) or ancient burial societies are early examples, non-life insurance really took off with mass markets after the great fire of London in 1666.
The most hyped example of insurtech in the non-life sector is the impact of technologies on the motor business like drive-less cars and car telematics. This paper from Swiss Re shows that the impact over the next 20 years of such advances on motor premia could be dramatic.
Much of the focus from insurtech innovation is on reducing expenses, an item that the industry is not light on. The graph below shows examples of the level of acquisition and overhead expenses in the non-life sector across different jurisdictions.
A recent report from Aon Benfield went further and looked at expenses across the value chain in the US P&C insurance sector, as below. Aon Benfield estimated overall expenses make up approximately half of gross risk premium, much of which represents juicy disruption targets for new technology in the insurtech world.
Insurance itself is based upon the law of large numbers and serves a socially useful function in reducing economic volatility by transferring risks from businesses and consumers. In 1906, Alfred Manes defined insurance as “an economic institution resting on the principle of mutuality, established for the purpose of supplying a fund, the need for which arises from a chance occurrence whose probability can be estimated”.
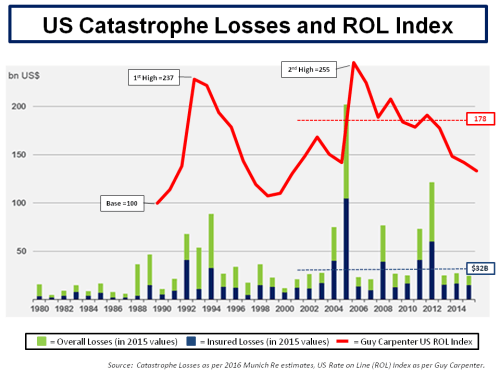
One of the issues identified with the current non-life insurance sector is the so-called protection gap. This is in effect where insurers’ risk management practises have got incredibly adapt at identifying and excluding those risks most likely to result in a claim. Although good for profits, it does bring the social usefulness of the transference of only the pristine risks into question (for everybody else). The graph below from Swiss Re illustrates the point by showing economic and insured losses from natural catastrophe events as a % of GDP.
It’s in the context of low investment returns and competitive underwriting markets (in themselves being driven by low risk premia across asset classes) that a new technology driven approach to the mutual insurance model is being used to attack expense and protection gap issues.
Mutuals represent the original business model for many insurers (back to burial schemes and the great fire of 1666) and still represent approximately a third of the sector in the US and Europe today. Peer to peer insurers are what some are calling the new technology driven mutuals. In fact, most of the successful P2P models to date, firms like Guevara, Friendsurance, and Inspeer are really intermediaries who pool consumers together for group discounts or self-financing of high deductibles.
Lemonade, which launched in New York this week, is a peer to peer platform which issues its own insurance policies and seeks to address the protection gap issue by offering broader coverage. The firm has been heavily reinsured by some big names in insurance like Berkshire Hathaway and Lloyd’s. It offers a fee based model, whereby the policyholders pay claims through mutualisation (assumingly by pools determined by pre-defined criteria). Daniel Schreiber, CEO and co-founder of Lemonade says that the firm will be ”the only insurer that doesn’t make money by denying claims”. Dan Ariely, a big deal in the world of Behavioral Economics, has been named as Chief Behavioral Officer, presumably in an effort to assist in constructing pools of well behaved policyholders.
The graphic below tries to illustrate how the business model is evolving (or should that be repeating?). Technology offers policyholders the opportunity to join with others to pool risk, hitherto a process that was confined to associations amongst professional groups or groups bound by location. Whether technology offers the same opportunity to underwrite risks profitably (or at least not at a loss) but with a larger reach remains to be seen.
It does occur to me that it may be successful in addressing areas of dislocation in the industry, such as shortfalls in coverage for flood insurance, where a common risk and mitigant can be identified and addressed in the terms of the respective pool taking the risks on.
For specialty re/insurers, we have already seen a bifurcation between the capital providers/risk takers and the risk portfolio managers in the ILS arena. Newer technology driven mutual based insurers also offer the industry a separation of the management of risk pools and the risk capital provided to underwrite them. I wish them well in their attempts at updating this most ancient of businesses and I repeat what I said in part 1 of this post – don’t let the sweet scent of shiny new technology distract you from the smell of the risk…..