So, after the (im)piety of the Christmas break, its time to reflect on 2014 and look to the new year. As is always the case, the world we live in is faced with many issues and challenges. How will China’s economy perform in 2015? What about Putin and Russia? How strong may the dollar get? Two other issues which are currently on traders’ minds as the year closes are oil and Greece.
The drop in the price of oil, driven by supply/demand imbalances and geo-political factors in the Middle East, was generally unforeseen and astonishing swift, as the graph of European Brent below shows.
click to enlarge
Over the short term, the drop will be generally beneficial to the global economy, acting like a tax cut. At a political level, the reduction may even put manners on oil dependent states such as Iran and Russia. Over the medium to long term however, it’s irrational for a finite resource to be priced at such levels, even with the increased supply generated by new technologies like fracking (the longer term environmental impacts of which remain untested). The impact of a low oil price over the medium term would also have negative environmental impacts upon the need to address our carbon based economies as highlighted in 2014 by the excellent IPCC reports. I posted on such topics with a post on climate models in March, a post on risk and uncertainty in the IPCC findings in April, and another post on the IPCC synthesis reports in November.
The prospect of another round of structural stresses on the Euro has arisen by the calling of an election in late January in Greece and the possible success of the anti-austerity Syriza party. Although a Greek exit from the Euro seems unlikely in 2015, pressure is likely to be exerted for relief on their unsustainable debt load through write offs. Although banking union has been a positive development for Europe in 2014, a post in May on an article from Oxford Professor Kevin O’Rourke outlining the ultimate need to mutualise European commitments by way of a federal Europe to ensure the long term survival of the Euro. Recent commentary, including this article in the Economist, on the politics behind enacting any meaningful French economic reforms highlights how far Europe has to go. I still doubt that the German public can be convinced to back-stop the commitments of others across Europe, despite the competitive advantage that the relatively weak Euro bestows on Germany’s exporting prowess.
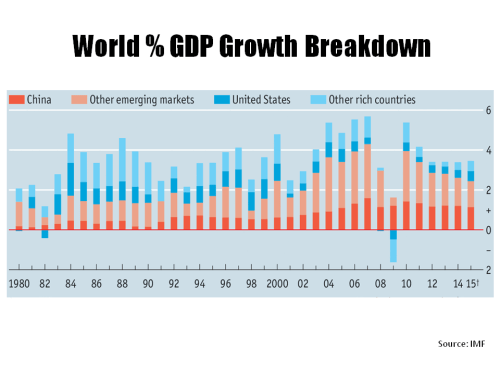
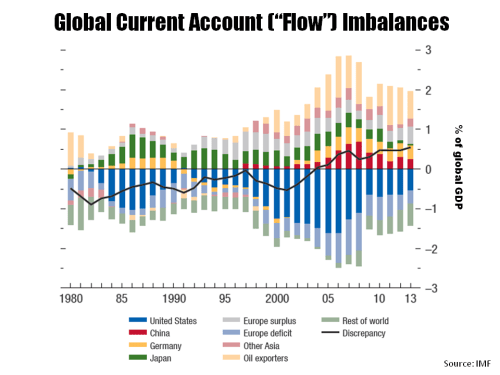
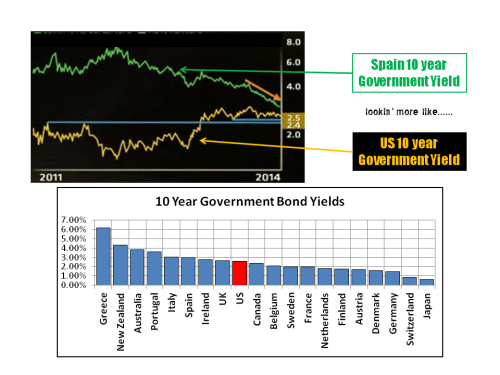
Perpetually, or so it seems, commentators debate the possible movements in interest rates over the coming 12 months, particularly in the US. A post in September on the findings of a fascinating report, called “Deleveraging, What Deleveraging?”, showed the high level of overall debt in the US and the rapid increase in the Chinese debt load. Although European debt levels were shown to have stabilised over the past 5 years, the impact of an aggressive round of quantitative easing in Europe on already high debt levels is another factor limiting action by the ECB. The impact of a move towards the normalisation of interest rates in the US on its economy and on the global economy remains one of the great uncertainties of our time. In 2015, we may just begin to see how the next chapter will play out.
Low interest rates have long been cited as a factor behind the rise in stock market valuations and any increase in interest rates remains a significant risk to equity markets. As the graph below attests, 2014 has been a solid if unspectacular year for nearly all equity indices (with the exception of the FTSE100), albeit with a few wobbles along the way, as highlighted in this October post.
click to enlarge
The debate on market valuations has been an ever-present theme of many of my posts throughout 2014. In a March post, I continued to highlight the differing views on the widely used cyclically adjusted PE (CAPE) metric. Another post in May highlighted Martin Wolf’s concerns on governments promoting cheap risk premia over an extended period as a rational long term policy. Another post in June, called Reluctant Bulls, on valuations summarized Buttonwood’s assertion that many in the market were reluctant bulls in the absence of attractive yields in other asset classes. More recently a post in September and a post in December further details the opposing views of such commentators as Jim Paulsen, Jeremy Siegel, Andrew Lapthorne, Albert Edwards, John Hussman, Philosophical Economics, and Buttonwood. The debate continues and will likely be another feature of my posts in 2015.
By way of a quick update, CAPE or the snappily named P/E10 ratio as used by Doug Short in a recent article on his excellent website shows the current S&P500 at a premium of 30% to 40% above the historical average. In his latest newsletter, John Hussman commented as follows:
“What repeatedly distinguishes bubbles from the crashes is the pairing of severely overvalued, overbought, overbullish conditions with a subtle but measurable deterioration in market internals or credit spreads that conveys a shift from risk-seeking to risk-aversion.”
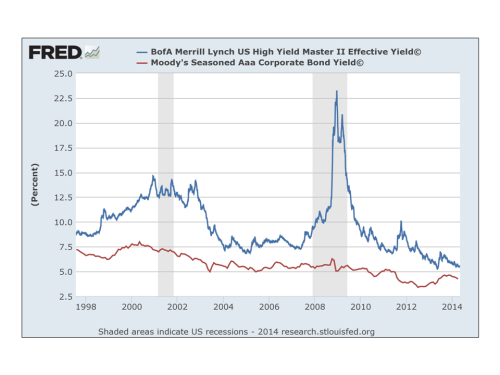
Hussman points to a recent widening in spreads, as illustrated by a graph from the St Louis Fed’s FRED below, as a possible shift towards risk aversion.
click to enlarge
The bull arguments are that valuations are not particularly stressed given the rise in earnings driven by changes to the mix of the S&P500 towards more profitable and internationally diverse firms. Critics counter that EPS growth is being flattered by subdued real wage inflation and being engineered by an explosion in share buybacks to the detriment of long term investments. The growth in quarterly S&P500 EPS, as illustrated below, shows the astonishing growth in recent years (and includes increasingly strong quarterly predicted EPS growth for 2015).
click to enlarge
A recent market briefing from Yardeni research gives a breakdown of projected forward PEs for each of the S&P500 sectors. Its shows the S&P500 index at a relatively undemanding 16.6 currently. In the graph below, I looked at the recent PE ratios using the trailing twelve month and forward 12 month operating EPS (with my own amended projections for 2015). It also shows the current market at a relatively undemanding level around 16, assuming operating EPS growth of approx 10% for 2015 over 2014.
click to enlarge
The focus for 2015 is therefore, as with previous years, on the sustainability of earnings growth. As a March post highlighted, there are concerns on whether the high level of US corporate profits can be maintained. Multiples are high and expectations on interest rates could make investors reconsider the current multiples. That said, I do not see across the board irrational valuations. Indeed, at a micro level, valuations in some sectors seem very rational to me as do those for a few select firms.
The state of the insurance sector made up the most frequent number of my posts throughout 2014. Starting in January with a post summarizing the pricing declines highlighted in the January 2014 renewal broker reports (the 2015 broker reports are due in the next few days). Posts in March and April and November (here, here and here) detailed the on-going pricing pressures throughout the year. Other insurance sector related posts focussed on valuation multiples (here in June and here in December) and sector ROEs (here in January, here in February and here in May). Individual insurance stocks that were the subject of posts included AIG (here in March and here in September) and Lancashire (here in February and here in August). In response to pressures on operating margins, M&A activity picking up steam in late 2014 with the Renaissance/Platinum and XL/Catlin deals the latest examples. When seasoned executives in the industry are prepared to throw in the towel and cash out you know market conditions are bad. 2015 looks to be a fascinating year for this over-capitalised sector.
Another sector that is undergoing an increase in M&A activity is the telecom sector, as a recent post on Europe in November highlighted. Level3 was one of my biggest winners in 2014, up 50%, after another important merger with TW Telecom. I remain very positive on this former basket case given its operational leverage and its excellent management with a strong focus on cash generation & debt reduction (I posted on TWTC in February and on the merger in June and July). Posts on COLT in January and November were less positive on its prospects.
Another sector that caught my attention in 2014, which is undergoing its own disruption, is the European betting and online gambling sector. I posted on that sector in January, March, August and November. I also posted on the fascinating case of Betfair in July. This sector looks like one that will further delight (for the interested observer rather than the investor!) in 2015.
Other various topics that were the subject of posts included the online education sector in February, Apple in May, a dental stock in August, and Trinity Biotech in August and October. Despite the poor timing of the August TRIB call, my view is that the original investment case remains intact and I will update my thoughts on the topic in 2015 with a view to possibly building that position once the selling by a major shareholder subsides and more positive news on their Troponin trials is forthcoming. Finally, I ended the year having a quick look at Chinese internet stocks and concluded that a further look at Google was warranted instead.
So that’s about it for 2014. There was a few other random posts on items as diverse as a mega-tsunami to correlations (here and here)!
I would like to thank everybody who have taken the time to read my ramblings. I did find it increasingly difficult to devote quality time to posting as 2014 progressed and unfortunately 2015 is looking to be similarly busy. Hopefully 2015 will provide more rich topics that force me to find the time!
A very happy and health 2015 to all those who have visited this blog in 2014.